1.What is Laser-Assisted Bonding (LAB)?
Laser Assisted Bonding (full name: Laser-assisted bonding, abbreviated as LAB) is a technology applied in the back-end packaging processes of semiconductor integrated circuits. Its principle involves using a laser beam to irradiate the die or device to be bonded, rapidly heating the die/device from room temperature to the bonding temperature within seconds, and then welding it onto a substrate, interposer, or another stacked die. This technology is suitable for advanced semiconductor packaging with high demands for speed, precision, and precise localized (or even micro-scale) heating control—for example, chip-to-substrate bonding and chip-to-wafer bonding. Compared to traditional reflow soldering and Thermal Compression Bonding (TCB), laser-based localized heating avoids thermal expansion without requiring additional measures. LAB exhibits significant advantages in bonding temperature, processing time, size of the heat-affected zone, and other aspects, making it the optimal choice for direct bonding of high-precision chips.
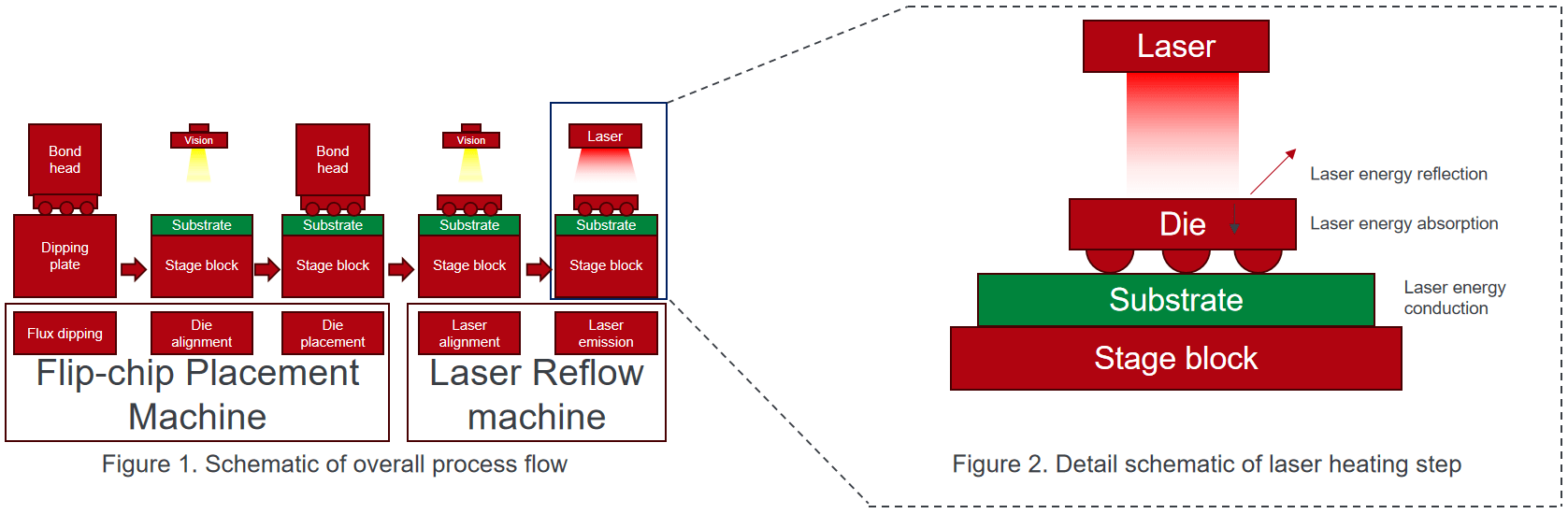
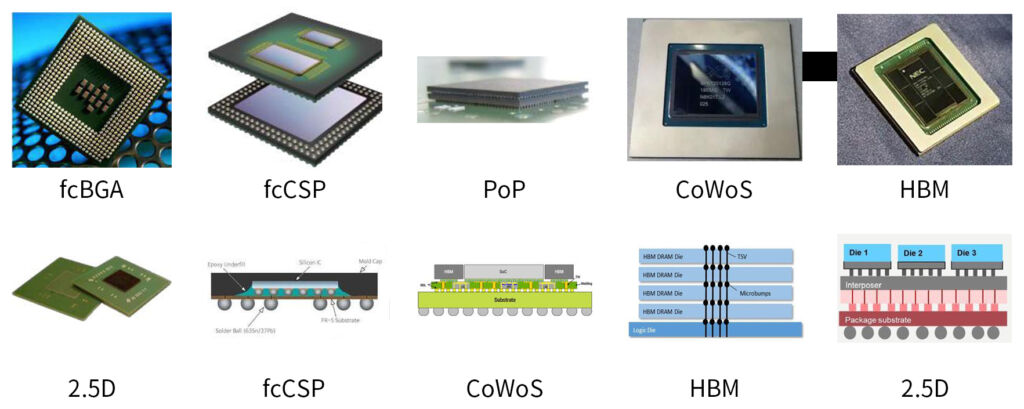
2.Typical Applications of Laser Assisted Bonding in Chip Packaging
3.Advantages of LAB Over Convection Ovens
① Convection ovens has significant disadv-antages for bonding thin and fine pitch dies:
- Soldering in a reflow oven leads to a high energy input into the product during the reflow process. The long duration of the reflow process is several minutes and heating affects the whole product.
- Thermal stress and warpage of chips and substrate are increased by exposing the whole workpiece to the reflow temperature for a prolonged period of time.
- Heat-sensitive components and substrates cannot be excluded from heating.
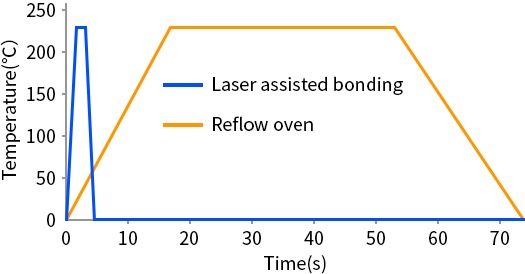
The image illustrates a comparison of the tempe-rature profiles for laser-assisted bonding and reflow oven processes.
Subjecting the entire wafer to extended heating can result in bending due to elevated thermal stress.
② Advantages of Laser Assisted Bonding (LAB):
- The heating process is brief and highly focused, leading to increased productivity.
- The heating process is more efficient and consumes less energy.
- The quality of the solder joints is improved, exhibiting less warping and lower thermal stress. Additionally, there is no thermal stress beyond the bonding interface, which reduces the risk of chip damage.
- It is suitable for a broader range of substrates, facilitating applications with narrower pitch. As the density of printed circuit boards continues to rise, this trend is expected to accelerate rapidly.
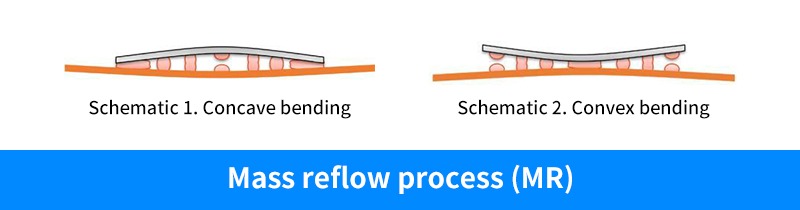
High thermal stress can lead to warping, resulting in three types of defective weld points:
① Non-welded points refer to the edges of Schematic 1 and the center of Schematic 2.
② Tensile weld points are illustrated in Schematic 1 and Schematic 2.
③ Bridge-type seams are illustrated in the center of Schematic 1 and along the edge of Schematic 2.
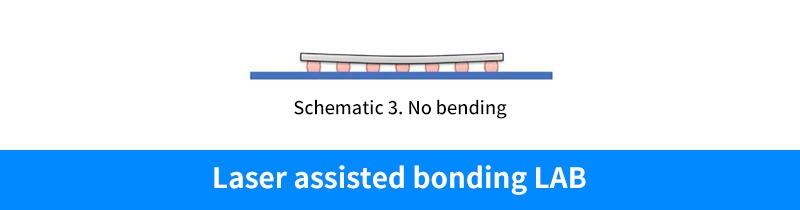
The thermal stress is minimal, and the weld joint is sound.
4.Advantages of LAB over Thermal Compression Bonding (TCB)
| Less energy input | Faster processes | Higher quality | |
| LAB |
|
|
|
| TCB |
|
|
|
5.Laser compression bonding
Laser Compression Bonding (LCB) is an advanced packaging technology that combines laser technology and thermo-compression bonding.
The laser compression bonding equipment includes components such as a transfer unit, a bonding head; the bonding head contains a bonding tool for applying pressure, a laser beam generator, a thermal imaging camera, and a compression unit for controlling the pressure and position; the laser beam generator is used to provide precise temperature control during the bonding process, and the thermal imaging camera is used to measure the temperature of semiconductor chips and substrates.
LCB technology is mainly used for semiconductor chip packaging, and its advantages include:
- Precise temperature control: The laser beam can provide localized heating, ensuring uniform and precise temperatures in the bonding area.
- Efficient production: Laser-assisted bonding speeds up the bonding process and increases productivity.
- High-quality bonding: Laser compression bonding provides a better surface finish and more uniform pressure distribution, resulting in improved bonding quality.
Compared to traditional hot press bonding, laser compression bonding is more precise in temperature control and reduces the risk of oxidization and contamination, thus improving the reliability and quality of the bond.
| Warpage control with vacuum tool | Solder height control | Rapid temp. ramp up | Rapid temp. ramp down | |
| LCB | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| TCB | √ | √ | √ | × |
 DYNALAS
DYNALAS