The miniaturization characteristics (50-200μm-scale dimensions) and high-density arrangement features of MiniLED chips pose dual challenges to the rework process:
1. Thermal zone precision bottleneck
Traditional equipment, due to insufficient thermal zone control precision, is highly prone to damaging adjacent components or substrate traces when removing faulty chips;
2. Thermodynamic control challenge
- The dual-pad structure of MiniLED requires simultaneous heating of both pad solder joints, but traditional reflow soldering rework can easily lead to: solder paste residue on pads (affecting the yield of secondary soldering);
- Local thermal stress accumulation causes micro-deformation of the substrate.
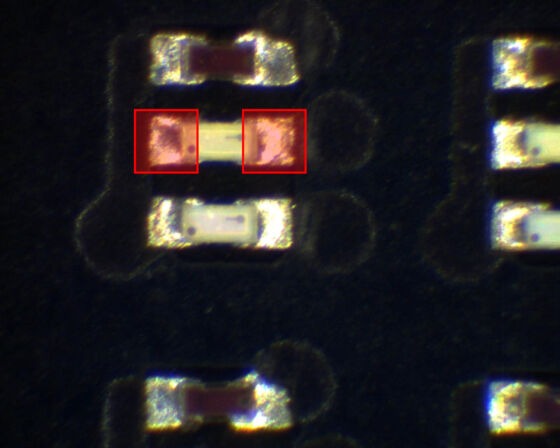
Challenging traditional welding methods, dual-spot technology enhances miniLED rework efficiency:
DYNALAS has long been dedicated to the field of precision laser heating systems, with its Laser-Assisted Bonding (LAB) system already widely adopted in the market. To improve the efficiency of miniLED rework, DYNALAS has developed a dual-spot laser system capable of simultaneously heating both ends of MiniLED chips, perfectly avoiding interference with the gap between the two solder pads on the substrate.
1.jpg)
LBS-mini: Dual-Spot Laser System
LBS-mini: Multiple Advantages of Dual-Spot Technology, Adaptable to Various Production Scenarios:
- A single laser light source can generate two spots;
- Simple structure with a more compact design, facilitating easy integration into production lines;
- Equipped with a closed-loop temperature control system;
- Unique optical shaping technology enables precise control over spot size;
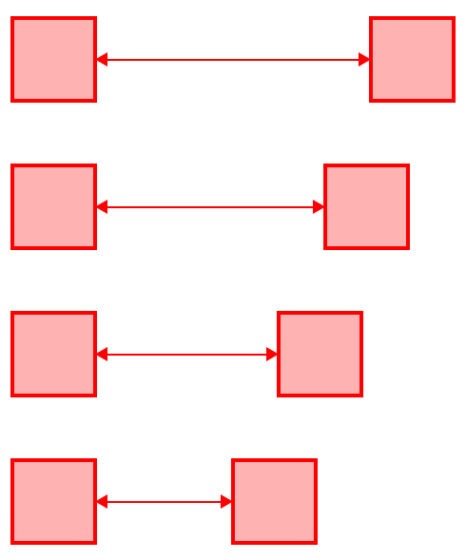
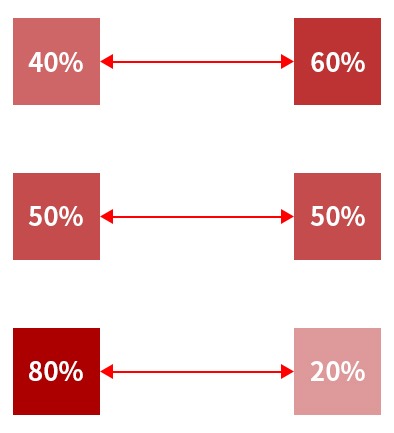
- Adjustable spot spacing and energy ratio.
 DYNALAS
DYNALAS